LLM Tracing
Quick Summary
LLM tracing allows you to easily debug LLM applications for both production monitoring and development evaluation environments at a component level. You should consider setting up tracing because tracing allows you to easily:
- debug failing test cases (ie. figure out how unsatisfactory
actual_outputs are generated during evaluation). - understand (in real-time) how LLM responses are generated when monitoring in production.
Confident AI is NOT tied to or vendor-locked into any LLM provider or framework, which means you can trace literally any LLM application of your choice.
Tracing Integrations
If your LLM application was built using a hybrid approach (eg., a bit of langchain, and bit of llama_index, and maybe a bit of custom LLM API calling), you'll want to consider custom tracing instead.
LlamaIndex
You can setup tracing for LLM applications built with LlamaIndex in 1 line of code:
from llama_index.core import set_global_handler
set_global_handler("deepeval")
The set_global_handler() function tells llama_index to trace via deepeval, which means LLM tracing will automatically be enabled and viewable on Confident AI for each llama_index query:
...
query_engine.query("...")
Custom Tracing
Custom tracing allows you to more flexibly define which part of your LLM application you want traced. There are a two main scenarios where custom tracing comes in handy:
- your LLM application wasn't built on any frameworks
- your LLM applicationi was built on multiple frameworks
In deepeval, tracing a particular component in your LLM application is as simple as adding a with block along with deepeval's Tracer in python.
from deepeval.tracing import Tracer, TraceType
...
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.LLM) as llm_trace:
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model='gpt-4o',
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "..."},
],
)
llm_response = response.choices[0].message.content
print(llm_response)
Nesting with blocks in python allows deepeval to recognize the trace hierarchy in your LLM application. For example, this trace structure:
from deepeval.tracing import Tracer, TraceType
with Tracer(trace_type="My LLM Application") as custom_trace:
...
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.RETRIEVER) as retriever_trace:
...
with Trace(trace_type=TraceType.EMBEDDING) as embedding_trace:
...
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.LLM) as llm_trace:
...
This particular nested with block will give the following structure:
My LLM Application
|
| --- Retriever
| |
| Embedding
|
| --- LLM
*
You'll notice the Tracer accepts a trace_type argument. The trace_type argument accepts either a str (for custom types of traces), or TraceType.
TraceType.LLM
TraceType.EMBEDDING
TraceType.RETRIEVER
TraceType.RERANKING
TraceType.SYNTHESIZE
TraceType.TOOL
TraceType.QUERY
TraceType.AGENT
TraceType.CHAIN
The trace_type parameter is an easy way for you to classify components in your pipeline and can either be of type TraceType, or str (for custom types). Here are all the TraceTypes that deepeval offers.
TraceType.AGENTTraceType.CHAINTraceType.CHUNKINGTraceType.EMBEDDINGTraceType.LLMTraceType.QUERYTraceType.RERANKINGTraceType.RETRIEVERTraceType.SYNTHESIZETraceType.TOOL
from deepeval.tracing import Tracer, TraceType
def llm(messages):
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.LLM) as llm_trace:
...
return llm_output
It is not necessary to define a TraceType ENUM for trace_type, as trace_type also accepts any string. However, there is no UI support for custom trace types as opposed to the ones defined above.
Set Parameters (Output and Metadata)
Before the end of each function, you must call the set_parameter method from the resource descriptor (llm_trace in the example above) in order to track the function output and any associated metadata. set_parameter accepts two arguments:
- [Required]
output: The output of your function, equivalent to the return value. - [Optional]
metadata: The metadata associated with the trace. The argument is available only if you are defining aTracerobject withtrace_typeasTraceType.EMBEDDINGorTraceType.LLM.
The example below defines an LLM with block and sets the output and metadata with the model name.
from deepeval.tracing import Tracer, TraceType, LlmMetadata
import openai
def llm(input_prompt):
# defining the with block with trace_type TraceType.LLM
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.LLM) as llm_trace:
# constructing the LLM response
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model='gpt-4-turbo-preview',
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful assistant.",
},
{"role": "user", "content": input_prompt},
],
)
output = response.choices[0].message.content
# calling set_parameters before the return statement
llm_trace.set_parameters(
output=output,
metadata=LlmMetadata(model='gpt-4-turbo-preview')
)
return output
Defining the metadata for LLM and EMBEDDING traces will help you easily view these parameters on the confident-AI platform.
The metadata for TraceType.EMBEDDING is the EmbeddingMetadata class, which consists of 1 optional variable: model of type string.
The metadata for TraceType.LLM is the LlmMetadata class, which consists of 5 optional variables:
model: stringtokenCount: dictionary with string keys and integer valuesoutputMessages: dictionary with string keys and string valuesllmPromptTemplate: not enforcedllmPromptTemplateVariables: not enforced
Setup Custom Tracing
In the previous section, you learned how to set up tracing for a single function. This section will
teach you how to set up tracing for your entire custom pipeline. First, import the Tracer object, TraceType, and the necessary metadata types from deepeval.tracing and set up the corresponding with blocks inside the functions/methods that make up your LLM pipeline.
Here's an implementation for a hypothetical LLM application utilizing deepeval's tracing support using Tracer objects through with blocks:
from deepeval.tracing import Tracer, TraceType, LlmMetadata, EmbeddingMetadata
import openai
class Chatbot:
def __init__(self):
pass
def llm(self, input_var):
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.LLM) as llm_trace:
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model='gpt-4-turbo-preview',
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful assistant.",
},
{"role": "user", "content": input_var},
],
)
output = response.choices[0].message.content
# calling set_parameters before the return statement
llm_trace.set_parameters(
output=output,
metadata=LlmMetadata(model='gpt-4-turbo-preview')
)
return output
def get_embedding(self, input_var):
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.EMBEDDING) as embedding_trace:
response = openai.Embedding.create(
input=input_var,
model="text-embedding-ada-002"
)
output = response['data'][0]['embedding']
# calling set_parameters before the return statement
embedding_trace.set_parameters(
output=output,
metadata=EmbeddingMetadata(model="text-embedding-ada-002")
)
return output
def retriever(self, input_var):
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.RETRIEVER) as retriever_trace:
embedding = self.get_embedding(input_var)
# Replace this with an actual vector search that uses embedding
list_of_retrieved_nodes = ["Retrieval Node 1", "Retrieval Node 2"]
# calling set_parameters before the return statement
embedding_trace.set_parameters(list_of_retrieved_nodes)
return list_of_retrieved_nodes
def search(self, input):
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.TOOL) as tool_trace:
# Replace this with an actual function that searches the web
title_of_the_top_search_results = "Search Result: " + input
# calling set_parameters before the return statement
tool_trace.set_parameters(title_of_the_top_search_results)
return title_of_the_top_search_results`
def format(self, retrieval_nodes, input):
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.TOOL) as tool_trace:
prompt = "You are a helpful assistant, based on the following information: \n"
for node in retrieval_nodes:
prompt += node + "\n"
prompt += "Generate an unbiased response for " + input + "."
# calling set_parameters before the return statement
tool_trace.set_parameters(prompt)
return prompt
def query(self, user_input):
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.AGENT) as tool_trace:
top_result_title = self.search(user_input)
retrieval_results = self.retriever(top_result_title)
prompt = self.format(retrieval_results, top_result_title)
output = self.llm(prompt)
# calling set_parameters before the return statement
tool_trace.set_parameters(output)
tool_trace.track(
event_name="Chatbot",
model='gpt-4-turbo-preview',
input=user_input,
response=output,
)
return output
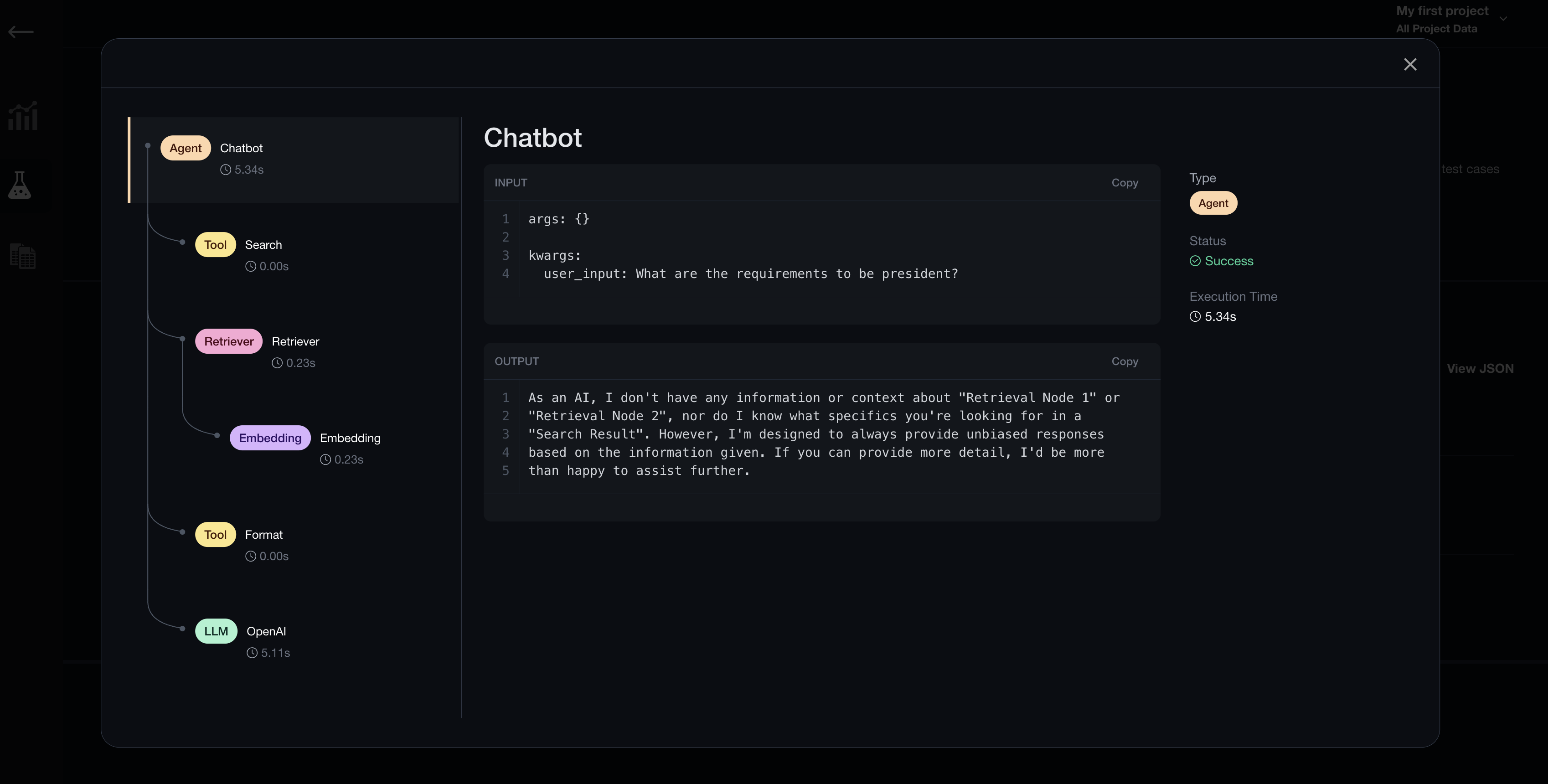
Setting up the with blocks using the Tracer object will automatically log LLM traces each time chatbot.query() (the outermost function of the example RAG pipeline) is called. This will allow you to debug failing test cases by inspecting individual trace stacks on the Confident AI platform.
Tracking
You might also notice that before the return statement in chatbot.query(), we call tool_trace.track() to track each event with the associated trace data. It is absolutely necessary to call this method because your trace data will not be recorded without it. This tracking method has the same exact arguments (and types) as deepeval.track. You can learn more about deepeval.track and tracking events here.
# calling set_parameters before the return statement
def query(self, user_input):
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.AGENT) as tool_trace:
...
tool_trace.set_parameters(output)
# you must call tool_trace.track() before returning the output
tool_trace.track(
event_name="Chatbot",
model='gpt-4-turbo-preview',
input=user_input,
response=output,
)
return output
This means that currently, tracing only works if you're tracking evaluations using the track method, and generating actual_outputs from your LLM application at evaluation time (ie. tracing does not work with pre-computed outputs).
Async Support
deepeval also supports asynchronous operations by tracking traces using context variables. This allows you to define your query function as an async function and simultaneously track different traces without interfering with each other.
# calling set_parameters before the return statement
async def query(self, user_input):
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.AGENT) as tool_trace:
...
return output
LlamaIndex Tracing
deepeval also supports automated tracing for RAG pipelines utilizing LlamaIndex with just a few lines of code. First, import set_global_handler from llama_index.core and set it to ‘deepeval’. Then, define a function to query from your query engine with a custom trace_type using the Tracer with block, and you’re done!
# llama_index pipeline dependencies
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader, Settings
from llama_index.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbedding
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
from llama_index.core import set_global_handler
set_global_handler("deepeval")
# set up your llama_index pipeline
Settings.llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-4-turbo-preview")
Settings.embed_model = OpenAIEmbedding(model="text-embedding-ada-002")
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("data").load_data()
node_parser = SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=200, chunk_overlap=20)
nodes = node_parser.get_nodes_from_documents(
documents, show_progress=True
)
index = VectorStoreIndex(nodes)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine(similarity_top_k=5)
# define chatbot function with custom trace_type
def chatbot(input):
with Tracer(trace_type="Chatbot") as chatbot_trace:
res = query_engine.query(input).response
chatbot_trace.set_parameters(res)
chatbot_trace.track(
event_name='llama_index chatbot'
input=input,
response=res,
model='gpt-4-turbo-preview',
)
return res
Setup Hybrid Tracing (Custom + LLamaIndex)
Lastly, deepeval supports hybrid tracing, combining custom tracing with LlamaIndex. To do so, set up custom tracing as you normally would. Simply import set_global_handler from llama_index.core and set it to ‘deepeval’. deepeval will handle all the logic behind the scenes and automatically nest the LlamaIndex traces in the correct trace positions.
Here's how you can set it up:
# llama_index dependencies
from llama_index.core.callbacks.base_handler import BaseCallbackHandler
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader
from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter
from llama_index.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbedding
from openai import AsyncOpenAI
from llama_index.core import set_global_handler
set_global_handler("deepeval")
class RAGPipeline:
def __init__(self, model_name="gpt-4-turbo-preview", top_k=5, chunk_size=200, chunk_overlap=20, min_similarity=0.5, data_dir="data"):
openai_key = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
if not openai_key:
raise ValueError("OpenAI API key not found in environment variables.")
self.openai_client = AsyncOpenAI(api_key=openai_key)
self.embed_model = OpenAIEmbedding(model="text-embedding-ada-002")
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(data_dir).load_data()
node_parser = SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=chunk_size, chunk_overlap=chunk_overlap)
nodes = node_parser.get_nodes_from_documents(documents, show_progress=True)
self.index = VectorStoreIndex(nodes, embed_model=self.embed_model)
self.retriever = self.index.as_retriever(similarity_top_k=top_k, similarity_cutoff=min_similarity)
self.model_name = model_name
def format_nodes(self, query):
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.NODE_PARSING) as llama_wrapper_trace:
nodes = self.retriever.retrieve(query)
combined_nodes = "\n".join([node.get_content() for node in nodes])
# set parameters
llama_wrapper_trace.set_parameters(combined_nodes)
return combined_nodes
async def generate_completion(self, prompt, context):
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.LLM) as llm_trace:
full_prompt = f"Context: {context}\n\nQuery: {prompt}\n\nResponse:"
response = await self.openai_client.chat.completions.create(
model=self.model_name,
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": full_prompt}
],
temperature=0.7,
max_tokens=200
)
output = response.choices[0].message.content
# set parameters
llm_trace.set_parameters(
output=output,
metadata=LlmMetadata(model='gpt-4-turbo-preview')
)
return output
async def aquery(self, query_text):
with Tracer(trace_type=TraceType.QUERY) as query_trace:
context = self.format_nodes(query_text)
response = await self.generate_completion(query_text, context)
# set parameters and track event
query_trace.set_parameters(response)
query_trace.track(
input=query_text,
response=response,
model='gpt-4-turbo-preview',
)
return response